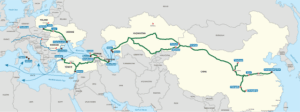
The Strategic Importance of Kazakhstan’s Trade Routes
Kazakhstan’s trade routes leverage its vast rail, road, and maritime network to connect to global markets in Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
Located at the heart of Central Asia, Kazakhstan has historically been a key player in trade routes due to its strategic location. It shares borders with countries such as China, Russia, Uzbekistan, and Kyrgyzstan.
Situated at the crossroads of the Silk Road, it played a pivotal role in connecting Asia with Europe through a network of trade routes spanning 6,000 km from 14 BC to 1450 AD.
This ancient trade route between the East and the West enabled the trade of goods like silk, spices, and other commodities. Thus, the country’s central location in Eurasia makes it a hub for trade between Europe and Asia.
In 2024, Kazakhstan is the:
- 48th largest economy worldwide
- 20th largest economy in Asia
- Largest economy in Central Asia
Kazakhstan’s top exports include crude oil, inorganic chemicals, iron & steel, cereals, and coppers. Top imports include vehicles, machinery, electrical machinery, pharmaceuticals, and plastics.
Furthermore, its top trading partners include China, the European Union, Russia, Türkiye, etc. Thus, the country’s central location in Eurasia makes it a hub for trade between Europe and Asia.
Kazakhstan Key Trade Routes & Partners
Kazakhstan’s trade routes leverage its strategic location between Europe and Asia.
Its vast trade routes establish it as an essential transit corridor for East-West and North-South trade, primarily through its ties with Russia, China, Europe, and the countries adjoining the Caspian Sea.
Here’s an overview of Kazakhstan’s primary trade routes and infrastructure:
- Trans-Caspian International Transport Route (Western European Route): Known as the “Middle Corridor,” this route links China to Europe through Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan, and the Caspian Sea. It facilitates the transport of goods from China to European markets, circumventing Russia.
- The North-South Corridor: An emerging trade route linking Kazakhstan with Russia & Iran. The route also helps trade flow from the Caspian Sea region to Persian Gulf ports, thus supporting trade with the Middle East, South Asia, and possibly Africa.
- Eurasian Land Bridge: Connects Kazakhstan to China in the east and Europe to the west. This route is a key transit corridor for goods moving between Asia and Europe.
- The China-Kazakhstan Railway Route: A major trade route between China and Kazakhstan. The railway connects Kazakhstan to China’s industrial regions.
- Kazakhstan-Russia Route: Russia is Kazakhstan’s largest neighbor, and rail & road connections across the border boost significant trade, especially in energy and natural resources such as oil, metals, and grains.
Read: The Strategic Importance of France’s Trade Routes
Kazakhstan Maritime Trade Routes
Kazakhstan’s maritime routes connect it to global markets across Asia and Europe.
Key Kazakhstan Ports
Although Kazakhstan is landlocked, it does have direct access to ports in Russia, China, and other Central Asian nations.
The critical ports related to Kazakhstan are:
- Aktau Port: Located on the Caspian Sea’s eastern shore, Kazakhstan’s main port for maritime trade on oil, grains and metals. Also, it connects with rail and road networks for broader trade routes. The port supports Kazakhstan’s trade with Iran, Türkiye, Turkmenistan, Russia, and Azerbaijan.
- Port of Kuryk: Kuryk port lies on the Caspian Sea coast in the Mangistau region of Kazakhstan. It supports the export of crude oil from the Kashagan oil fields (Kazakhstan) to Baku in Azerbaijan, where it is transported to Türkiye through the BTC oil pipeline. Also, it plays a significant role in the Belt and Road Initiative, linking China to Europe.
- Khorgos Dry Port: located near Kazakhstan’s border with China, it is a vital part of the Belt and Road Initiative for trade between China, Central Asia, and Europe. It serves as a significant gateway for containerized goods and bulk cargo.
- Bautino Port: Situated in southwestern Kazakhstan near the Bautino Bay of the Tyubkaragansky Gulf, it is a logistics hub for energy projects in the Caspian Sea.
- Other Kazakhstan Ports: Öskemen, Atyrau, Semey, Aktobe.
- Via Russia: Kazakhstan uses Russian ports like, Olya, Astrakhan, Novorossiysk (Black Sea) and St. Petersburg (Baltic Sea) for trade with Russia, Europe and the Mediterranean.
- Via China: Key ports such as Lianyungang and Shanghai enable Kazakhstan to access East Asia and international markets.
Major Maritime Routes and Trading Regions
- Caspian Sea Route: Kazakhstan uses the Caspian Sea as its primary maritime gateway, connecting to regional and global trade routes. It links Kazakhstan to ports in other Caspian countries. They include Azerbaijan (Baku), Turkmenistan (Turkmenbashi), Russia (Astrakhan), and Iran (Bandar Anzali).
- Trans-Caspian International Transport Route: This trade route is often called the “Middle Corridor. Thus, it connects China through Kazakhstan to the Caspian Sea, then to Azerbaijan, Georgia, Türkiye, and Europe. The route reduces dependency on Russian transport and is part of China’s Belt and Road Initiative.
- Neighbouring Ports for Global Access:
- Russia: Kazakhstan uses the Port of Novorossiysk on the Black Sea for oil and grain exports.
- China: Kazakhstan benefits from access to the port of Lianyungang, a key route for trade with the Asia-Pacific region.
- Iran: Kazakhstan connects to Iran’s Bandar Abbas port along the Persian Gulf for trade with South Asia and beyond.
Main Export Commodities via Maritime Routes
- Energy: Crude oil, natural gas, and coal.
- Metals: Uranium, copper, zinc.
- Agricultural Products: Wheat, barley, and other grains.
- Others: chemicals, fertilizers, machinery, consumer goods
Key Trading Partners & Regions
- European Union: Accessed via the Black Sea and Baltic routes, focusing on oil, gas, and metals.
- China: A major partner through the Belt and Road Initiative, exporting energy and raw materials.
- Middle East: Utilizes Persian Gulf routes, trading fertilizers, grains, and energy.
- South Asia: Accessed through Iran, targeting Indian and regional markets.
- Türkiye and the Caucasus: Serves as a bridge to Europe via the Trans-Caspian corridor.
Kazakhstan Air Cargo Routes
Kazakhstan Land Routes
Kazakhstan’s land trade routes connect it with major European and Asian cities, boosting trade through overland routes. Key roads include:
- Trans-Caspian International Transport Route: Links China to Europe via Kazakhstan, the Caspian Sea, Azerbaijan, and Türkiye. It is also known as the Middle Corridor.
- Route runs from China through Kazakhstan, crossing the Caspian Sea into Azerbaijan, and continues through Georgia and Türkiye into Europe.
- Consists of multimodal transport (rail, sea, and road).
- Important hubs: Khorgos Gateway (Kazakhstan-China border) and Aktau Port (Caspian Sea).
- Western Europe-Western China Corridor: A major highway and rail link connecting China to Western Europe through Kazakhstan.
- Part of China’s Belt and Road Initiative – China-Europe Overland Route.
- It spans from Germany through Russia and Kazakhstan, terminating in the Chinese city of Lianyungang.
- With an overland transit time of about 10 days from Europe to China, the highway provides a significantly quicker alternative to sea routes, which take up to 45 days.
- North-South Corridor (Russia and Central Asia) – Under Development: This multimodal route aims to connect India, Iran, and Russia with Kazakhstan using Iran as a gateway to the Persian Gulf and South Asia.
- The North-South corridor will support bilateral trade between Russia, Central Asia, and beyond, particularly to South Asia and the Middle East.
- NSC will incorporate multiple transport modes, including rail, road, and maritime routes.
Types of Goods Exported via Land Routes
- Metals & Minerals: Iron, steel, copper, zinc, gold, bauxite, lead, and aluminium.
- Energy Products: Crude oil, refined petroleum, coal, uranium, and natural gas.
- Agricultural Products: Sunflower, rapeseed oils, beef, and lamb.
- Industrial Goods: Machinery and Equipment.
- Dairy Products: Milk and cheese.
- Fresh Produce: fruits and vegetables.
Major Trade Destinations
- China: the world’s largest trading nation, facilitated by the Belt and Road Initiative. A major destination for Kazakhstan’s energy exports, mainly crude oil, coal, and natural gas.
- Russia: Close economic ties with Kazakhstan under the Eurasian Economic Union. Moscow imports agricultural products and consumer goods from Kazakhstan.
- Europe: Kazakhstan exports a variety of goods to European countries, including metals, energy, chemicals, and machinery.
- Central Asia: Kazakhstan has close trade ties with neighbouring countries like Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Turkmenistan.
- Middle East: With trade routes through Iran and Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan also supplies agricultural products and energy to the region
Kazakhstan Rail Routes
- China: Kazakhstan’s top trading partner. Imports crude oil, coal, and minerals from Kazakhstan and exports consumer goods and industrial products.
- Russia: Facilitates the majority of Kazakhstan’s European-bound trade. Also, it imports consumer goods, machinery, and chemicals from Kazakhstan.
- European Union: A destination for Kazakhstan goods like metals, crude oil, and agricultural products.
- Central Asia and the Middle East: Provides connectivity for regional trade and access to seaports.
Kazakhstan Oil & Gas Pipeline Routes
Due to its vast oil and gas reserves, Kazakhstan is a major player in the global energy market. Thus, the country’s pipeline network is vital for exporting crude oil & gas to Asia and Europe.
Below are detailed overview of Kazakhstan’s oil & gas pipeline routes:
- Kazakhstan-China Oil Pipeline: The pipeline starts from the Atasu oil terminal in Western Kazakhstan to China’s Xinjiang region.
- Length: Approximately 2,800 km
- Capacity: 20 million tons of oil per year
- Significance: This pipeline is strategic for Kazakhstan’s oil export to China, one of the world’s largest oil consumers. It diversifies Kazakhstan’s export routes away from Russia and provides direct access to the Chinese market.
- Caspian Pipeline Consortium Pipeline: The CPC pipeline links Kazakhstan’s Tengiz oil field to the Russian port of Novorossiysk on the Black Sea.
- Length: 1,510 km
- Capacity: Approximately 67 million tons
- Significance: The CPC pipeline is the principal route for Kazakhstan’s oil exports to Europe and the Mediterranean region.
- Central Asia-China Gas Pipeline: The pipeline runs from Turkmenistan to Kazakhstan’s gas fields and continues through Kazakhstan to China.
- Length: Over 1,833 km, but Kazakhstan’s portion is about 1,000 km long.
- Capacity: Approximately 55 billion cubic meters of gas annually.
- Significance: This pipeline connects Kazakhstan to China’s gas market, enabling gas exports from Kazakhstan to China.
- Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan (BTC) Pipeline (via Kazakhstan’s connection to Azerbaijan): The BTC pipeline links the Caspian Sea region to Turkey, with oil arriving in Baku, Azerbaijan, then transported through Georgia to Ceyhan, a port on the Mediterranean.
- Length: Approximately 1,768 km
- Capacity: 1 million barrels per day
- Significance: Although not entirely within Kazakhstan, the BTC pipeline connects Kazakhstan’s oil to global markets via Azerbaijan and Türkiye. Thus, it adds to Kazakhstan oil export routes.
Kazakhstan Key Trading Partners
- China: Kazakhstan’s largest trading partner and investor, primarily through the Belt and Road Initiative. China imports oil, gas, and minerals from Kazakhstan. In return, Kazakhstan imports machinery, electronics, and textiles from China.
- Russia and the Eurasian Economic Union: Kazakhstan’s EAEU membership provides duty-free access to member states.
- The European Union: The EU is an emerging trading partner. The EU imports Kazakhstan’s oil and metals and exports machinery, chemicals, and equipment.
- Türkiye: Kazakhstan exports oil, gas, and minerals to Türkiye and import from Türkiye machinery, textiles, and consumer goods.
- Central Asia: The trade between Kazakhstan and its neighbouring countries includes energy, agricultural products, and industrial goods.
- India: India is a growing trade partner for Kazakhstan. Kazakhstan exports energy, while India exports pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and engineering products.